TOPEKA, Kan. — Kansas could soon offer up to $5 million in grants for schools to outfit surveillance cameras with artificial intelligence systems that can spot people carrying guns. But the governor needs to approve the expenditures and the schools must meet some very specific criteria.
The AI software must be patented, “designated as qualified anti-terrorism technology,” in compliance with certain security industry standards, already in use in at least 30 states and capable of detecting “three broad firearm classifications with a minimum of 300 subclassifications” and “at least 2,000 permutations,” among other things.
Only one company currently meets all those criteria: the same organization that touted them to Kansas lawmakers crafting the state budget. That company, ZeroEyes, is a rapidly growing firm founded by military veterans after the fatal shooting at Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Florida.
The legislation pending before Kansas Gov. Laura Kelly highlights two things. After numerous high-profile shootings, school security has become a multibillion-dollar industry. And in state capitols, some companies are successfully persuading policymakers to write their particular corporate solutions into state law.
ZeroEyes also appears to be the only firm qualified for state firearms detection programs under laws enacted last year in Michigan and Utah, bills passed earlier this year in Florida and Iowa and legislation proposed in Colorado, Louisiana and Wisconsin.
On Friday, Missouri became the latest state to pass legislation geared toward ZeroEyes, offering $2.5 million in matching grants for schools to buy firearms detection software designated as “qualified anti-terrorism technology.”
“We’re not paying legislators to write us into their bills,” ZeroEyes co-founder and Chief Revenue Officer Sam Alaimo said. But “if they’re doing that, it means I think they’re doing their homework, and they’re making sure they’re getting a vetted technology.”
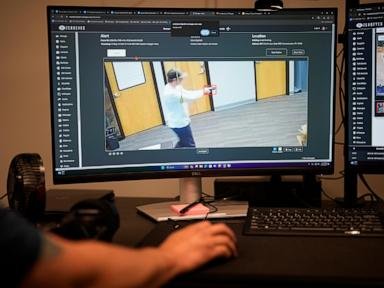
ZeroEyes uses artificial intelligence with surveillance cameras to identify visible guns, then flashes an alert to an operations center staffed around the clock by former law enforcement officers and military veterans. If verified as a legitimate threat by ZeroEyes personnel, an alert is sent to school officials and local authorities.
The goal is to “get that gun before that trigger’s squeezed, or before that gun gets to the door,” Alaimo said.
Few question the technology. But some do question the legislative tactics.
The super-specific Kansas bill — particularly the requirement that a company have its product in at least 30 states — is “probably the most egregious thing that I have ever read” in legislation, said Jason Stoddard, director of school safety and security for Charles County Public Schools in Maryland.
Stoddard is chairperson of the newly launched National Council of School Safety Directors, which formed to set standards for school safety officials and push back against vendors who are increasingly pitching particular products to lawmakers.
When states allot millions of dollars for certain products, it often leaves less money for other important school safety efforts, such as electronic door locks, shatter-resistant windows, communication systems and security staff, he said.
“The artificial-intelligence-driven weapons detection is absolutely wonderful,” Stoddard said. “But it’s probably not the priority that 95% of the schools in the United States need right now.”
The technology also can be costly, which is why some states are establishing grant programs. In Florida, legislation to implement ZeroEyes technology in schools in just two counties cost a total of about $929,000.
ZeroEyes is not the only company using surveillance systems with artificial intelligence to spot guns. One competitor, Omnilert, pivoted from emergency alert systems to firearms detection several years ago and also offers around-the-clock monitoring centers to quickly review AI-detected guns and pass alerts onto local officials.
But Omnilert does not yet have a patent for its technology. And it has not yet been designated by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security as an anti-terrorism technology under a 2002 federal law providing liability protections for companies. It has applied for both.
Though Omnilert is in hundreds of schools, its products aren’t in 30 states, said Mark Franken, Omnilert’s vice president of marketing. But he said that shouldn’t disqualify his company from state grants.
Franken has contacted the Kansas governor’s office in hopes she will line-item veto the specific criteria, which he said “create a kind of anti-competitive environment.”
In Iowa, legislation requiring schools to install firearms detection software was amended to give companies providing the technology until July 1, 2025, to receive federal designation as an anti-terrorism technology. But Democratic state Rep. Ross Wilburn said that designation was originally intended as an incentive for companies to develop technology.
“It was not put in place to provide, promote any type of advantage to one particular company or another,” Wilburn said during House debate.
In Kansas, ZeroEyes’ chief strategy officer presented an overview of its technology in February to the House K-12 Education Budget Committee. It included a live demonstration of its AI gun detection and numerous actual surveillance photos spotting guns at schools, parking lots and transit stations. The presentation also noted authorities arrested about a dozen people last year directly as a result of ZeroEyes alerts.
Kansas state Rep. Adam Thomas, a Republican, initially proposed to specifically name ZeroEyes in the funding legislation. The final version removed the company’s name but kept the criteria that essentially limits it to ZeroEyes.
House K-12 Budget Committee Chair Kristey Williams, a Republican, vigorously defended that provision. She argued during a negotiating meeting with senators that because of student safety, the state couldn’t afford the delays of a standard bidding process. She also touted the company’s technology as unique.
”We do not feel that there was another alternative,” Williams said last month.
The $5 million appropriation won’t cover every school, but Thomas said the amount could later increase once people see how well ZeroEyes technology works.
“I’m hopeful that it does exactly what we saw it do and prevents gun violence in the schools,” Thomas told The Associated Press, “and we can eventually get it in every school.”
___
Lieb reported from Jefferson City, Missouri. Associated Press writer Hannah Fingerhut contributed from Des Moines, Iowa.